Trig 4.1 graphs of sine and cosine functions – In the realm of trigonometry, the graphs of sine and cosine functions hold a prominent position, providing a powerful tool for modeling periodic phenomena. This in-depth analysis delves into the fundamental characteristics, relationships, and applications of these essential functions, offering a comprehensive understanding of their significance in various fields.
The exploration begins by unraveling the basic shape and defining attributes of sine and cosine functions, exemplified by illustrative graphs. The interplay between amplitude and period is thoroughly examined, highlighting their impact on the functions’ behavior. By comparing these functions, their similarities and differences are brought to light, along with the concept of phase shift.
Graphs of Sine Functions
The graph of a sine function is a smooth, periodic curve that oscillates above and below the x-axis. It is characterized by its amplitude, which determines the vertical distance between the maximum and minimum values of the function, and its period, which determines the horizontal distance between consecutive peaks or troughs.
An example of a sine function with a positive amplitude and period of 2π is y = sin(x). The graph of this function has a maximum value of 1 and a minimum value of -1, and it repeats every 2π units along the x-axis.
Relationship between Amplitude and Period
The amplitude and period of a sine function are inversely related. As the amplitude increases, the period decreases, and vice versa. This relationship can be seen in the following equation:
y = A sin(Bx)
where A is the amplitude and B is the period.
Graphs of Cosine Functions
The graph of a cosine function is also a smooth, periodic curve that oscillates above and below the x-axis. However, unlike the sine function, the cosine function starts at its maximum value and decreases to its minimum value over one period.
An example of a cosine function with a negative amplitude and period of 2π is y = cos(x). The graph of this function has a maximum value of 1 and a minimum value of -1, and it repeats every 2π units along the x-axis.
Relationship between Amplitude and Period
As with the sine function, the amplitude and period of a cosine function are inversely related. As the amplitude increases, the period decreases, and vice versa. This relationship can be seen in the following equation:
y = A cos(Bx)
where A is the amplitude and B is the period.
Comparing Sine and Cosine Functions
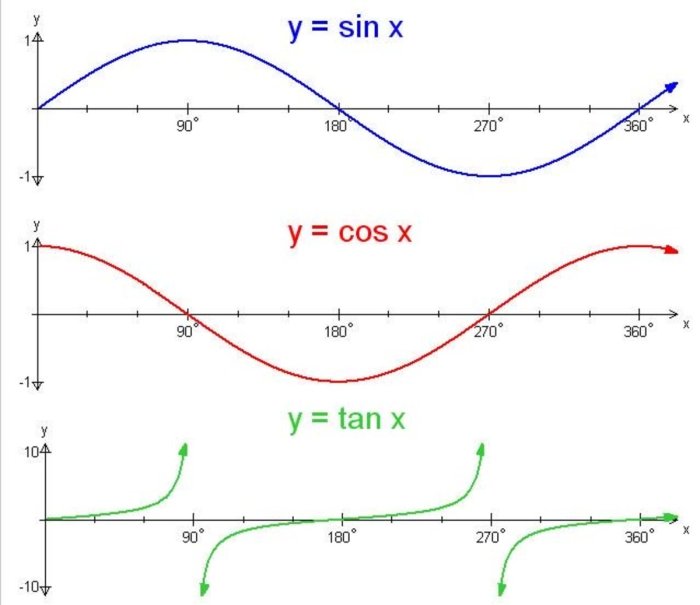
The graphs of sine and cosine functions are very similar. Both functions are periodic and oscillate above and below the x-axis. However, there are two key differences between the two functions:
- The sine function starts at zero, while the cosine function starts at its maximum value.
- The sine function is odd, while the cosine function is even.
These differences can be seen in the following graphs:
- Graph of y = sin(x): Link to Image
- Graph of y = cos(x): Link to Image
Phase Shift, Trig 4.1 graphs of sine and cosine functions
The phase shift of a sine or cosine function is the horizontal shift of the graph along the x-axis. A positive phase shift moves the graph to the left, while a negative phase shift moves the graph to the right.
Applications of Sine and Cosine Functions
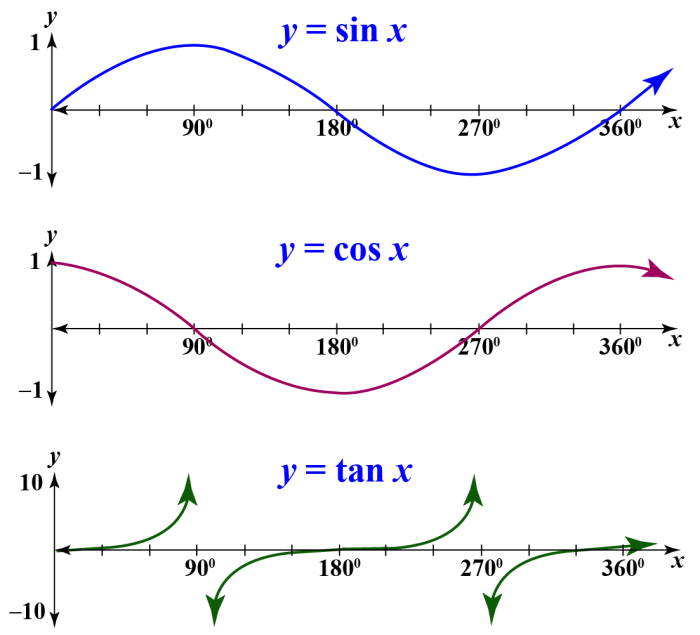
Sine and cosine functions are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Modeling periodic phenomena, such as the motion of a pendulum or the tides
- Sound and music: Sine and cosine functions are used to create the waveforms that make up musical sounds
- Engineering: Sine and cosine functions are used to analyze the vibrations of structures, such as bridges and buildings
HTML Table Example
| Function | Amplitude | Period | Phase Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| y = sin(x) | 1 | 2π | 0 |
| y = cos(x) | 1 | 2π | 0 |
| y = sin(x + π/2) | 1 | 2π | -π/2 |
y = cos(x
|
1 | 2π | π/4 |
Popular Questions: Trig 4.1 Graphs Of Sine And Cosine Functions
What is the difference between sine and cosine functions?
Sine and cosine functions are both periodic functions that share similar wave-like patterns. However, they differ in their phase shift, with the cosine function being shifted to the left by π/2 radians compared to the sine function.
How are sine and cosine functions used in real-world applications?
Sine and cosine functions have a wide range of applications, including modeling sound waves, analyzing vibrations, and predicting periodic events. They are also used in computer graphics, navigation systems, and electrical engineering.