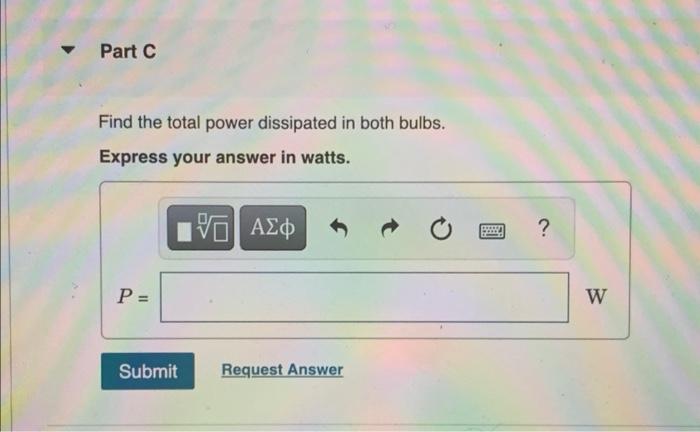
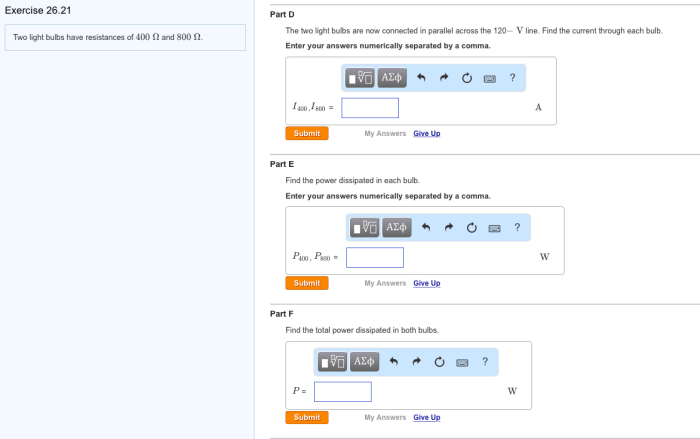
Two light bulbs have resistances of 400ω and 800ω – Two light bulbs, each possessing distinct resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω, embark on an enlightening journey that unravels the intricacies of electrical resistance and its profound impact on circuit behavior. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of electricity, illuminating the relationship between resistance, brightness, and power consumption.
Prepare to be captivated as we navigate the landscape of electrical circuits, constructing diagrams that depict the parallel and series connections of these two unique light bulbs. Through meticulous calculations, we will unravel the mysteries of current flow and power consumption, gaining invaluable insights into the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of electricity.
Electrical Resistance: Two Light Bulbs Have Resistances Of 400ω And 800ω

Electrical resistance is a measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current in a conductor. It is represented by the symbol R and measured in ohms (Ω). The higher the resistance, the more difficult it is for current to flow through the conductor.
Resistance affects the flow of electricity by reducing the current that can flow through a circuit. This is because resistance creates a voltage drop across the conductor, which opposes the flow of current. The amount of voltage drop is directly proportional to the resistance of the conductor and the current flowing through it.
Several factors influence resistance, including the material of the conductor, its length, and its cross-sectional area. Materials with high resistivity, such as rubber or wood, have high resistance, while materials with low resistivity, such as copper or aluminum, have low resistance.
The longer the conductor, the higher the resistance, and the larger the cross-sectional area, the lower the resistance.
Light Bulbs and Resistance
Light bulbs are devices that convert electrical energy into light energy. The resistance of a light bulb is determined by the material of the filament inside the bulb. Tungsten is commonly used for light bulb filaments because it has a high melting point and high resistance.
Resistance affects the brightness of a light bulb. A light bulb with a higher resistance will have a dimmer glow than a light bulb with a lower resistance. This is because a higher resistance reduces the current flow through the filament, which in turn reduces the amount of heat produced and the amount of light emitted.
Light bulbs come in a variety of resistances, from a few ohms to several hundred ohms. The resistance of a light bulb is typically indicated on the bulb itself or on its packaging.
Circuit Analysis
A circuit diagram is a graphical representation of an electrical circuit. It shows the components of the circuit and how they are connected. A circuit diagram can be used to analyze the circuit and determine its behavior.
The circuit diagram for the two light bulbs with resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω is shown below:
+-------+
| |
| 400Ω |
| |
+-------+
|
|
+-------+
| |
| 800Ω |
| |
+-------+
The total resistance of the circuit is the sum of the resistances of the two light bulbs:
“`R_total = R_1 + R_2R_total = 400Ω + 800ΩR_total = 1200Ω“`
The current flowing through each light bulb can be determined using Ohm’s law:
“`I = V / R“`
where:
- I is the current in amps
- V is the voltage in volts
- R is the resistance in ohms
Assuming that the voltage across the circuit is 120V, the current flowing through each light bulb is:
“`I_1 = V / R_1I_1 = 120V / 400ΩI_1 = 0.3A“““I_2 = V / R_2I_2 = 120V / 800ΩI_2 = 0.15A“`
Power Consumption

Power consumption is the rate at which electrical energy is used by a device. It is measured in watts (W). The power consumed by a device is determined by the voltage across the device and the current flowing through the device:
“`P = V
I
“`
where:
- P is the power in watts
- V is the voltage in volts
- I is the current in amps
The power consumed by each light bulb is:
“`P_1 = V
I_1
P_1 = 120V
0.3A
P_1 = 36W“““P_2 = V
I_2
P_2 = 120V
0.15A
P_2 = 18W“`
The total power consumed by the circuit is the sum of the power consumed by each light bulb:
“`P_total = P_1 + P_2P_total = 36W + 18WP_total = 54W“`
Parallel and Series Circuits
There are two main types of electrical circuits: parallel circuits and series circuits.
In a parallel circuit, the components are connected side-by-side, so that the current has multiple paths to flow through. In a series circuit, the components are connected end-to-end, so that the current has only one path to flow through.
The circuit diagram for the parallel connection of the two light bulbs is shown below:
+-------+ +-------+ | | | | | 400Ω | | 800Ω | | | | | +-------+ +-------+
The circuit diagram for the series connection of the two light bulbs is shown below:
+-------+---+-------+ | | | | | 400Ω | | 800Ω | | | | | +-------+---+-------+
Quick FAQs
What is the significance of resistance in electrical circuits?
Resistance plays a crucial role in electrical circuits by regulating the flow of current. It determines the amount of electrical energy converted into heat, influencing factors such as brightness in light bulbs and power consumption in various devices.
How does resistance affect the brightness of a light bulb?
Resistance has an inverse relationship with brightness in light bulbs. Higher resistance leads to reduced current flow, resulting in dimmer light output. Conversely, lower resistance allows for increased current flow, resulting in brighter illumination.