Embark on an educational journey with our Animal Cell Organelles and Structures Worksheet, a meticulously crafted resource designed to illuminate the intricate workings of animal cells. Delve into the fascinating world of cellular biology, where organelles, the functional units of cells, orchestrate a symphony of life-sustaining processes.
As we unravel the secrets of the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and a myriad of other organelles, you will gain a profound understanding of their roles in regulating substance movement, controlling cell activities, and orchestrating protein synthesis and energy production.
Prepare to be captivated by the elegance and complexity of animal cell architecture.
Animal Cell Organelles and Structures Overview: Animal Cell Organelles And Structures Worksheet
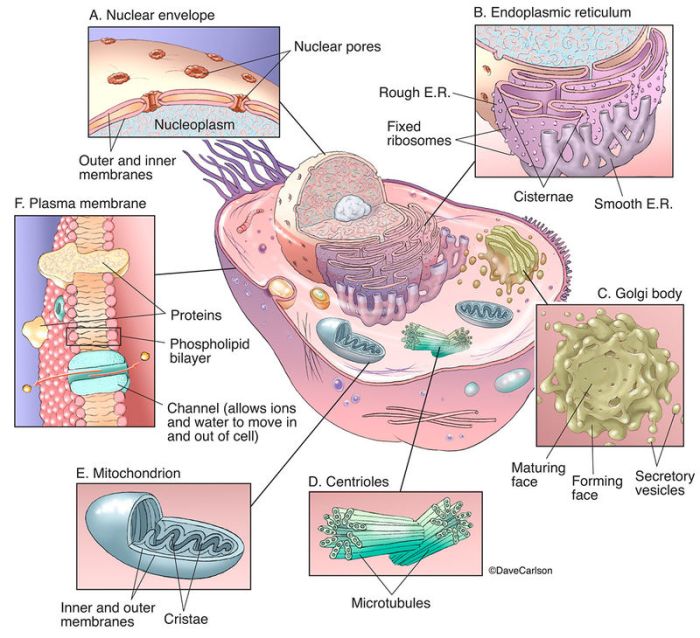
Animal cells are the basic unit of life for animals. They are composed of a variety of organelles, each of which has a specific function. Organelles are essential for cell function, and they work together to maintain the cell’s homeostasis.
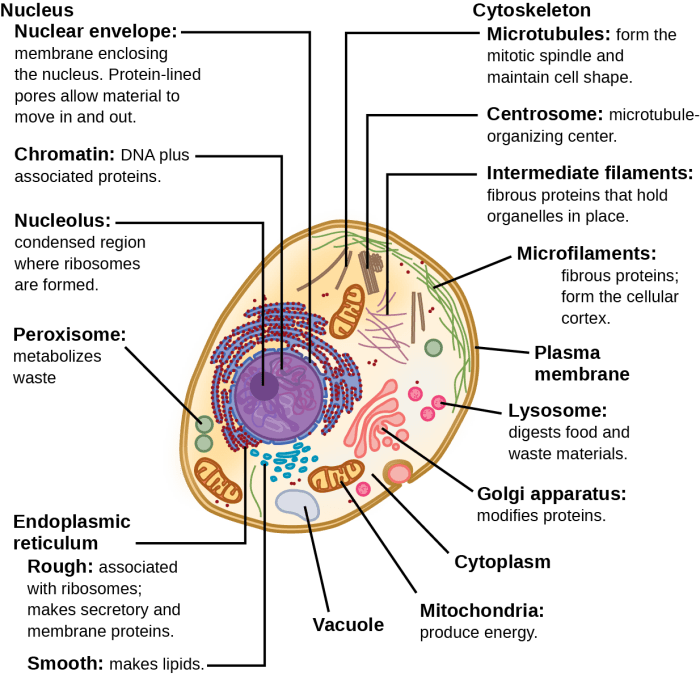
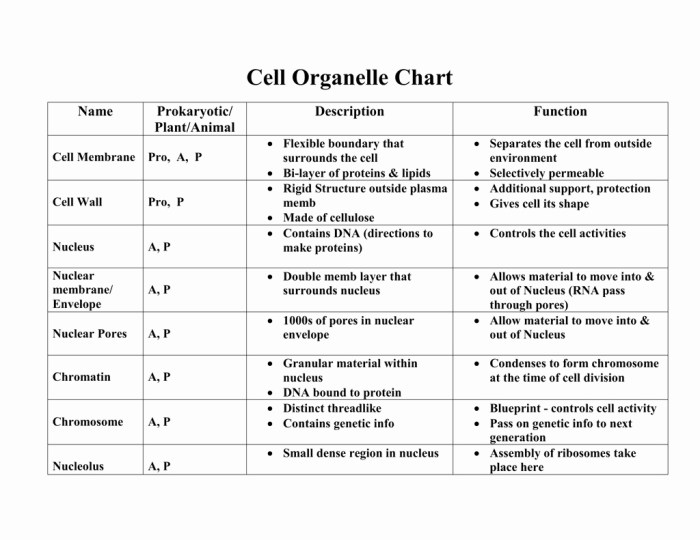
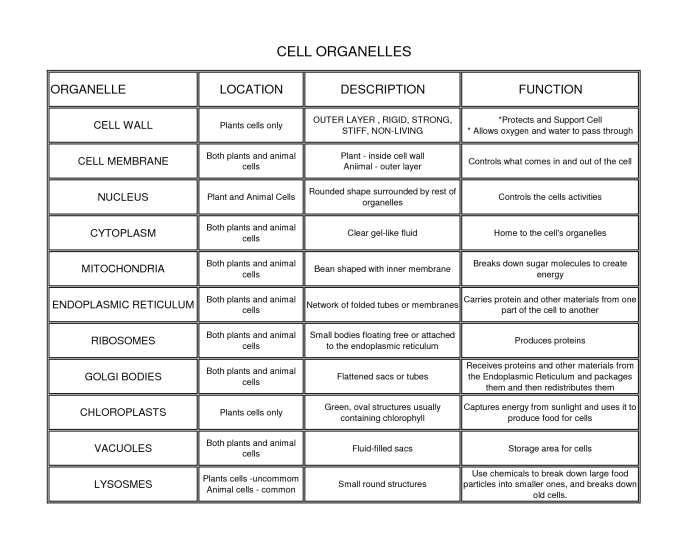
- The cell membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell. It protects the cell from its surroundings and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
- The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell. It contains all of the cell’s organelles.
- The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the cell’s DNA.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins.
- The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened sacs that modifies and packages proteins.
- The mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They produce energy for the cell.
- The lysosomes are small sacs that contain digestive enzymes. They break down waste products and recycle them into useful materials.
- The ribosomes are small particles that make proteins.
- The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that gives the cell its shape and helps it to move.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell. It protects the cell from its surroundings and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads face outward, while the hydrophobic tails face inward. This arrangement creates a barrier that prevents water-soluble molecules from passing through the membrane.The cell membrane also contains proteins.
These proteins perform a variety of functions, including:
- Transporting molecules across the membrane
- Recognizing and binding to other cells
- Signaling to other cells
Cytoplasm and Cytosol, Animal cell organelles and structures worksheet
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell. It contains all of the cell’s organelles.The cytosol is the liquid portion of the cytoplasm. It contains a variety of molecules, including:
- Enzymes
- Proteins
- Nucleotides
- Ions
The cytosol is the site of many important cellular processes, including:
- Glycolysis
- Protein synthesis
- DNA replication
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the cell’s DNA.The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope is a double membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.The nucleus contains a number of structures, including:
- Chromosomes
- Nucleolus
- Nuclear matrix
Chromosomes are long, thin structures that contain the cell’s DNA. DNA is the genetic material that determines the cell’s characteristics.The nucleolus is a small, dense structure that is located within the nucleus. The nucleolus is the site of ribosome production.The
nuclear matrix is a network of fibers that gives the nucleus its shape and supports the other structures within the nucleus.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins.There are two types of ER:
- Rough ER
- Smooth ER
Rough ER is covered with ribosomes. Ribosomes are small particles that make proteins. The proteins that are made on the rough ER are folded and transported to the Golgi apparatus.Smooth ER does not have ribosomes. It is involved in a variety of cellular processes, including:
- Lipid synthesis
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Detoxification
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier, regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
What is the role of the nucleus in cellular activities?
The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, housing the genetic material (DNA) and directing protein synthesis.
How do ribosomes contribute to protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are responsible for assembling amino acids into polypeptide chains, the building blocks of proteins.